An Expert’s Guide to the Salary Slip Format [with Samples]
Posted On:- 5 August, 2025 By:- Vaibhav Maniyar
Introduction
Ever stared at the password-protected PDF from HR, wondering how the allowances and the deductions all means? The numbers for Basic, HRA, and Special Allowance adding up on one side, while PF and Professional Tax are subtracted on the other is a simple overview, but the details lie in getting these numbers there at the start. That’s why, this password-protected document, your salary slip, is one of the most important financial documents today. This guide is written to help you understand the salary slip format common in India. Not only we’ll break down every component and provide different samples, but also answer all your pressing questions, so you can understand exactly where your money comes from and where it goes.
What is a Salary Slip?
Definition: A salary slip (also called a pay stub or payslip) is a document that shows your monthly earnings, deductions, and net pay. It serves as proof of income and helps you understand how your gross salary (CTC) converts to in-hand (take home) Salary. It systematically lists the various components of earnings (like basic salary and allowances) and deductions (like taxes and provident fund), ultimately showing the final net amount paid to the employee. In simple words, this salary slip format is a legal proof of income and employment.
Sample Salary Slip Formats [India]
Not all payslips look the same. The level of detail and presentation can vary. Let's compare the three salary slips from three different companies.
1. Traditional Simple Format
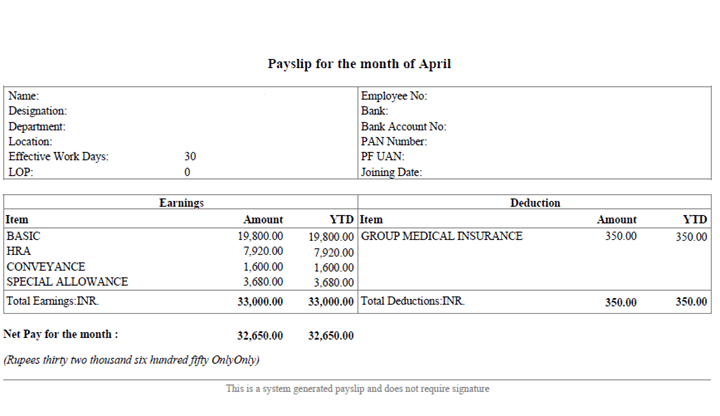
Earnings
Basic Salary: ₹19,800 (60% of total earnings)
HRA (House Rent Allowance): ₹7,920 (24% of total earnings)
Conveyance Allowance: ₹1,600 (4.8% of total earnings)
Special Allowance: ₹3,680 (11.2% of total earnings)
Total Earnings: ₹33,000
Deductions
Group Medical Insurance: ₹350
Total Deductions: ₹350
Net Pay: ₹32,650
What's Good
YTD (Year-to-Date) tracking for tax planning
Reasonable HRA component at 24%
What's Missing
No EPF (Employee Provident Fund) deduction - This is legally required for most employees
No professional tax deduction
No income tax deduction (TDS)
Missing ESI (Employee State Insurance) for this salary range
Red Flag: The absence of statutory deductions suggests this might be a contract position or the company isn't complying with labour laws.
2. Comprehensive Corporate Format
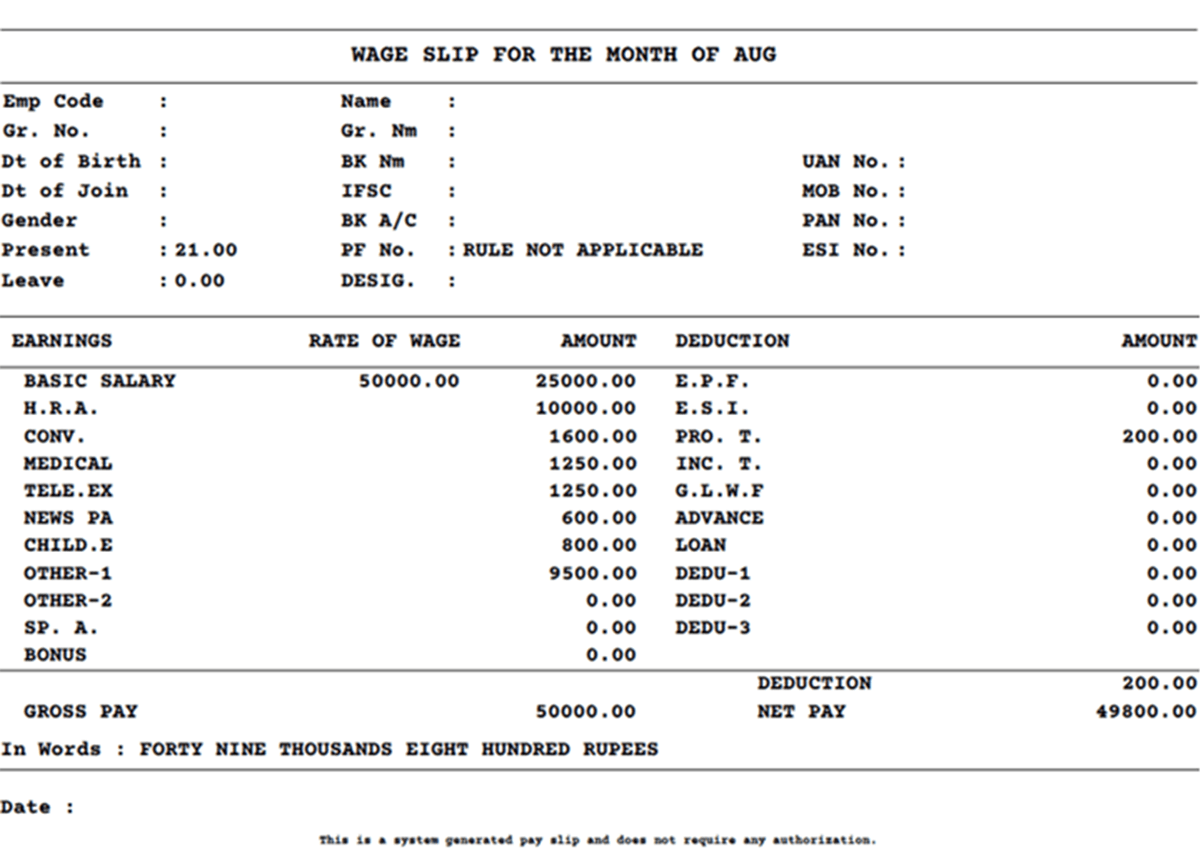
Earnings
Basic Salary: ₹25,000 (50% of gross)
HRA: ₹10,000 (20% of gross)
Conveyance: ₹1,600
Medical: ₹1,250
Telephone/Internet : ₹1,250
Newspaper: ₹600
Child Education: ₹800
Other Allowances: ₹9,500
Gross Pay: ₹50,000
Deductions
Professional Tax: ₹200
Total Deductions: ₹200
Net Pay: ₹49,800
What's Excellent
Professional tax compliance
Good basic-to-gross ratio (50%)
Tax-friendly allowance structure
Critical Missing Elements:
No EPF deduction (should be ₹3,000 for ₹25,000 basic)
No TDS despite ₹50,000 monthly salary
No ESI (though salary might be above ESI limit)
Tax Implication: Without proper EPF deduction, the employee loses tax benefits under Section 80C.
3. Professional Services Format
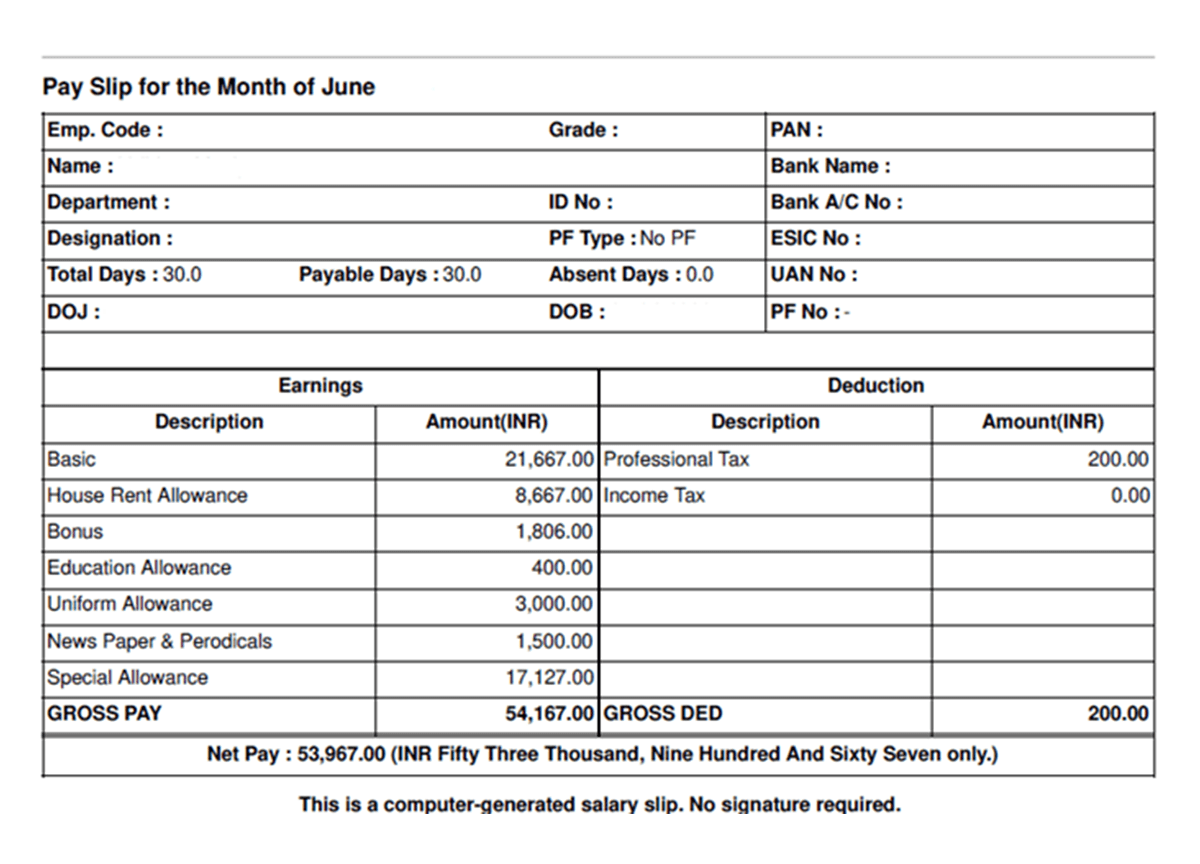
Earnings
Basic: ₹21,867 (40.5% of gross)
House Rent Allowance: ₹8,667 (16% of gross)
Bonus: ₹1,806
Education Allowance: ₹4000
Uniform Allowance: ₹3,000
News Paper & Periodicals: ₹1,500
Special Allowance: ₹17,127
Gross Pay: ₹54,167
Deductions
Professional Tax: ₹200
Income Tax: ₹0 (TDS)
Total Deductions: ₹200
Net Pay: ₹53,967
What's Best
Professional tax compliance
Income tax line item (even if zero)
Education and uniform allowances for tax benefits
Major Concerns:
No EPF deduction on ₹21,867 basic salary
Zero income tax seems incorrect for a ₹54,167 monthly salary
Missing ESI (salary above ₹21,000 limit)
Salary Slip Format Summary Table
| Feature | Traditional | Corporate | Professional |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structure | Modern, concise tabular format | Traditional, detailed (resembles dot-matrix reports); includes detailed sections; visually more crowded | Modern, dense tabular; extensive columns for earnings and deductions |
| Header Info | Clear with company, employee ID, month, YTD details | Classic, includes pay period, employee code, department, bank info; generally richer in classic payroll fields | Clear, has company and employee section, period, and totals, but skips some legacy fields |
| Earnings Breakdown | Simple, core heads: Basic, HRA, Conveyance, Special Allowance; no extra perks | Broad: Basic, HRA, Conveyance, Medical, Telephone, News Paper, Education, Children Edu., Bonus, Other-1,2, Special Allowance, etc | Most varied: Basic, HRA, Special Allowance, Bonus, News Paper & Periodicals, Education, Uniform, etc |
| Deduction Details | Minimal: Only Group Medical Insurance shown deducted | Detailed: Professional Tax, PF, ESI, Income Tax, Advance/Loan, multiple deduction slots, with many fields at 0 | Only main statutory deductions like Professional Tax and Income Tax; fewer deduction heads shown |
Related: Salary Arrears in India: Meaning, Calculation, Format & Tax Rules Explained
How to Create a Salary Slip Format from Scratch?
From payroll processing to compliance standpoint, designing a salary slip format is about more than just listing numbers. It's about building a compliant, transparent, and efficient remuneration structure. Here is the professional approach to structuring employee compensation.
The process begins with the Cost to Company (CTC), which is the total budget allocated per employee. This CTC must be broken down strategically to balance statutory compliance, tax efficiency for the employee, and company liability.
Step 1: Establishing the Core Components
Basic Salary: As a standard industry practice and to ensure compliance with various labour laws, the basic salary should be set at 40-50% of the total CTC. This percentage is critical as it directly impacts statutory calculations like provident fund and gratuity.
House Rent Allowance (HRA): To enable employees to claim tax benefits under Section 10(13A) of the Income Tax Act, HRA is typically structured as 40% (for non-metros) or 50% (for metro cities) of the basic salary. Structuring it this way aligns with the conditions for HRA exemption.
Statutory Bonuses & Other Fixed Allowances: Allocate amounts for any mandatory bonuses or fixed allowances as per company policy or employment contracts.
Special Allowance:This component serves as the balancing figure. It is calculated as:
Special Allowance = Total CTC - (Basic Salary + HRA + Other Allowances + Employer's PF Contribution)
It is a fully taxable component used to ensure the employee's total earnings align with the agreed-upon CTC.
Step 2: Incorporating a Flexible Benefit Plan (FBP)
To improve the value proposition for employees, an FBP can be designed within the CTC, allowing employees to choose from a pool of tax-efficient allowances based on their needs, especially if they are under the old tax regime. As an HR/Finance professional, you would structure these options:
Meal Vouchers/Coupons:
Can be offered up to the tax-exempt limit of ₹2,200 per month.
Mobile & Internet Reimbursement:
Offered on an actual-bill-submission basis, often capped at a policy limit (e.g., ₹3,000 per month).
Books and Periodicals:
Provided as a reimbursement against bills, typically up to ₹1,000 per month.
Other Components:
Allowances for education (₹100/month/child) or uniforms (as per policy) can also be included in the FBP.
The final salary slip format must clearly itemise all these earnings and the corresponding deductions to provide a complete and auditable record.
What are the Red Flags in a Salary Slip Format?
For a payroll professional, a "red flag" on a salary slip is a symptom of a potential compliance failure or a process error that can expose the organisation to legal and financial risk. Here are the critical issues to monitor:
Non-compliant Statutory Deductions
This is the most severe risk. It includes:
- 1. Failure to deduct EPF for eligible employees.
- 2. Non-deduction of ESI for employees whose gross pay is within the statutory limit.
This can lead to significant penalties, interest on late payments, and legal action from the EPFO and ESIC.
Improper Basic Salary Ratio
A Basic Salary that is artificially low (e.g., below 30-40% of CTC) to reduce PF liability is a major compliance risk, especially in light of Supreme Court rulings on PF on allowances. It leads to incorrect statutory calculations and potential retrospective liabilities.
Incorrect TDS Calculation and Remittance
Deducting too little tax (TDS) based on an employee's income and investment declarations can result in a notice from the Income Tax Department for short deduction. This makes the employer liable for the shortfall, along with interest and penalties.
Absence of Year-to-Date (YTD) Figures
A salary slip format lacking YTD figures indicates poor payroll software or process. YTD data is essential for internal audits, payroll reconciliation, accurate Form 16 generation, and providing employees with a clear financial summary. Its absence is a sign of a deficient system.
Standard Salary Slip Format Checklist
Checking a salary slip is a core part of the monthly payroll reconciliation process. It ensures accuracy and compliance before payroll is disbursed and records are finalised. The process involves seven key checks at appropriate timelines:
PF Calculation
Confirm the employee and employer PF contributions are calculated precisely at 12% of the "PF Wages" (typically Basic + DA). Any deviation requires immediate investigation.
(PT) Slab Compliance
Ensure the PT deduction aligns with the specific state's slab rates. This is often ₹200 per month, but may vary (e.g., ₹300 in February in some states).
TDS Declarations
The TDS amount must be calculated based on the employee's chosen tax regime and the investment proofs submitted. It should not be an arbitrary estimate. The payroll system must accurately prorate annual tax liability over the remaining months.
YTD Data Verification
Ensure that the YTD figures for gross earnings, taxable income, and all deductions have been correctly rolled up from the previous month. This is critical for end-of-year reporting.
ECR (Electronic Challan cum Return)
After remitting PF contributions, the amounts in the filed ECR on the EPFO portal must match the deduction figures in the payroll register. This closes the loop on PF compliance for the month.
TDS Remittance
Periodically cross-check that the TDS amounts deposited by the company are accurately reflected against each employee's PAN in their Form 26AS on the income tax e-filing portal. This prevents future discrepancies for employees during ITR filing.
Adherence to Internal Compensation Policies
Finally, audit the payslip components (like HRA, Special Allowance) against the approved internal compensation policies and the employee's offer letter to ensure there are no contractual deviations.
Related: How ESS Helps to Provide Job Satisfaction?
Create and Deliver Salary Slip Effortlessly – Powered by Minop
For businesses, ensuring every employee receives an accurate, timely, and secure payslip is a major responsibility. The manual processes of calculating payroll, handling deductions, and individually sending out payslips are prone to errors and delays.
This is where MINOP steps in and automates the entire process.
MINOP is a cutting-edge, cloud-based time and attendance and payroll software that automates this entire workflow. It eliminates human error and ensures compliance. For employees, this means the end of chasing HR. A few days after salary credit, MINOP automatically emails a detailed, password-protected salary slip directly to your personal email ID. This keeps your sensitive financial data secure, private, and always available to you.
FAQs
What is the difference between UAN and PF Number?
UAN (Universal Account Number) is a permanent 12-digit number that links all your PF accounts from different jobs. A PF Number is specific to an employer and changes when you switch jobs.
Is a Salary Slip Mandatory by Law in India?
Yes. Under the Payment of Wages Act, 1936, and various state-level Shops and Establishment Acts, employers are legally required to provide a payslip to their employees. It can be a physical copy or an electronic one.
Can I Get a Loan Without a Salary Slip?
It is extremely difficult. Banks and lenders consider your last 3-6 months of salary slips as the primary proof of stable income. Without them, it is nearly impossible to get approved for a home loan, car loan, personal loan, or credit card, as your repayment capacity cannot be verified.
What is the standard salary slip format in India?
The standard salary slip format in India includes employee and employer details, a breakdown of earnings (such as Basic Salary, HRA, Special Allowance), and statutory deductions (EPF, TDS, Professional Tax). It shows the gross and net salary for the pay period and is issued monthly.
Can I download a salary slip format in India?
Yes, many websites offer downloadable salary slip templates. You can also ask your HR for a standard salary slip in PDF or Excel format. This blog includes a sample format as a reference.
How to calculate take-home pay from a salary slip?
Subtract total deductions (PF, PT, TDS) from the gross salary. Net Salary = Gross Salary - Deductions.

Comments