How to Prepare MIS Report from Cloud-Based HR Software?
Posted On:- 28 October, 2025 By:- Vaibhav Maniyar
Introduction
Management Information System or an MIS Report is a key document which summarizes or interprets data, later impacting decision-making and strategic planning. These reports are designed for different purposes and can be created manually or using specialized software, specifically, a cloud-based attendance platform. Without such a platform, the last week of the month can become an overwhelming and stressful period for both HR and accounts teams.
A smarter solution is to connect biometric devices via API to a time and attendance application, allowing teams to handle leave requests and attendance corrections before the payroll deadline. The final, accurate data is then seamlessly sent to HR and finance, ensuring error-free payroll processing.
In this blog, you’ll learn how to prepare an MIS report, explore its different types, and understand the essential KPIs every HR team should track for smarter decision-making.
What Is an MIS Report? (Full Form + Meaning Explained)
Definition: MIS stands for Management Information System. An HR MIS report consolidates raw attendance, leave, and overtime data into organized, actionable information that supports HR decision-making and payroll processing. Modern MIS reports are not created by entering data manually; they are downloaded and combined or merged based on requirements, whether for payroll or for investigating employee attendance history.
Quick Fact:
If the application you are using has a dedicated Android or iOS app that tracks employees through geolocation, the MIS report can even include the location from which they clocked in. This feature is extremely helpful for auditing the expense tracking of field sales employees.
So, what makes a standard MIS report different from a simple data export?
A standard data export of punch-in records, leave entries, overtime hours, and millions of other metrics might get the job done when you need to pinpoint a specific problem or use the data to help make a final decision. However, a Management Information System report takes its final form and shows an attendance summary by employee with totals, consolidates all leave types with balances, and calculates overtime while flagging policy violations.
In short, you have trained and designed the software in such a way that the cloud-based, real-time attendance system does everything, auditing from the core and finding issues without taking much time. The key difference is that an MIS report is pre-processed and organized specifically for your workflow, whether that's payroll processing, compliance audits, or management reviews.
Related: Why Corporates Should Switch to Cloud Based HR Systems?
Why MIS Reports Matter
MIS reports highlight important performance indicators, showing how a company is doing financially, operationally, and in the market. These reports also point out areas that need improvement and guide teams toward achieving their goals.
One of the biggest advantages of MIS reports is that they make decision-making easier and more accurate. They help identify risks and opportunities, whether it’s planning for growth, launching new products, or spotting falling sales. For instance, financial MIS reports can reveal cash flow and profitability trends, helping the company use its resources wisely.
MIS reports also improve communication across the organization. When information is summarized clearly, employees, managers, and even investors can understand how the company is performing. This transparency builds trust and encourages collaboration.
Another important benefit is that MIS reports show trends and patterns over time, which is valuable for long-term planning. Businesses can anticipate challenges, spot opportunities, and stay competitive.
Regularly creating MIS reports keeps companies agile and ensures decisions are based on facts, not guesswork.
How many types of MIS Reports are there?
Depending on the data, an MIS report can tackle a variety of different projections. These projections are broadly classified into eight different sub-categories, each with different variations altogether.
Summary MIS Reports
Trend MIS Reports
Profit MIS Reports
Inventory MIS Reports
Cashflow MIS Reports
MIS Reports in Accounting
Sales MIS Reports
Exception MIS Reports
Apart from these eight types, one important report type includes performance reports which measure employee productivity. These reports tackle employee in-out, monthly attendance, overtime and a bunch of other types of time and attendance reports. A performance report is usually generated via a software.
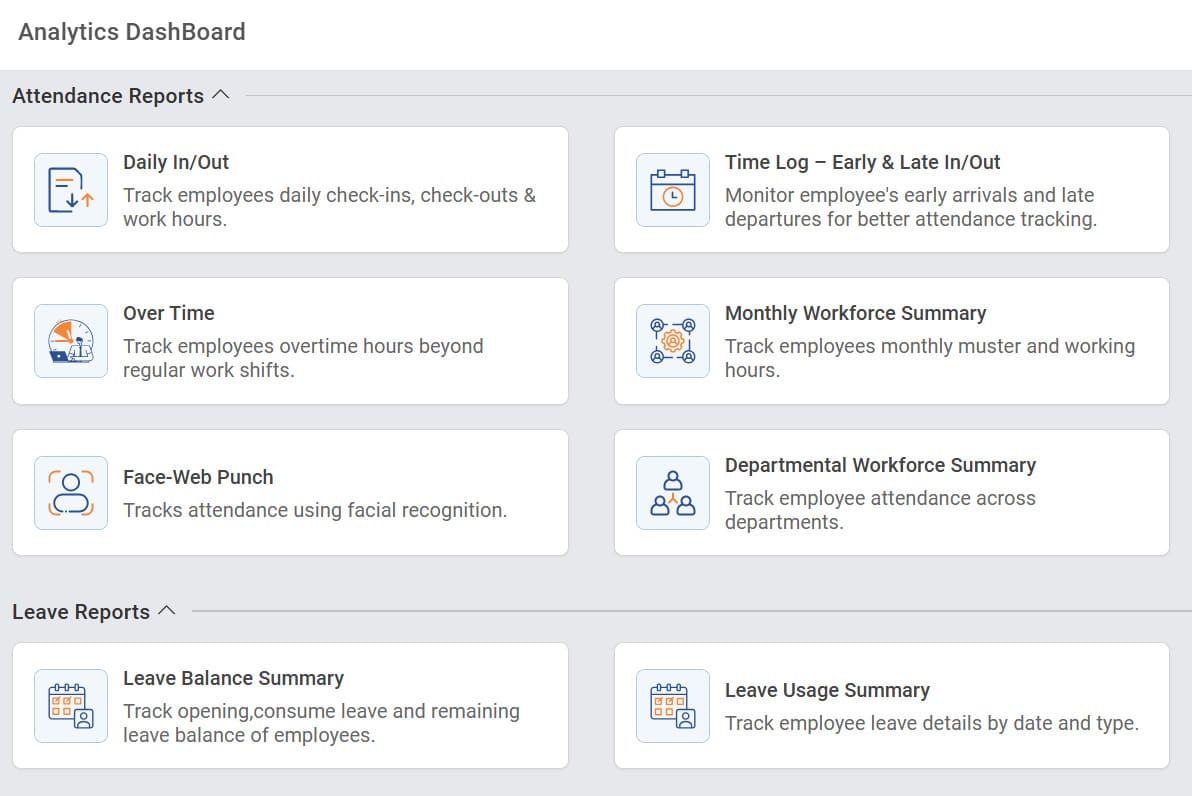
For example, MINOP’s analytics dashboard shows a section-wise, segregated reporting style where managers or HR professionals can generate various time, attendance, and leave reports without needing to manually compile data.
Here, the data is already synced in real-time through biometric devices, perfectly illustrating how a complex array of data is made accessible through a user-friendly interface, with each option representing a specific type of MIS report.
How to Make HR MIS Report Using Time and Attendance Software
Before cloud-based applications, HR managers and other small-to-medium companies had employee monitoring software installed on a workforce analytics platform. The primary objective was to keep employees as productive and engaged as possible. For instance, the timer would stop or a warning would be issued if the mouse was not moved or a key was not pressed. In the end, the software created sheets of data that were eventually turned into MIS reports. However, the process was extremely exhausting and outdated.
Instead of Copying and Customizing: Download MIS Reports from MINOP by Filtering Different Departments, Employees, Weeks/Months Seamlessly.
Now, due to the advent and mass use of biometric devices, data flows easily to cloud-based attendance systems, and HR professionals can create MIS reports with a one-click download.
step
Filter by Date
Select the kind of MIS report needed and apply the month or past-month filter to segregate by department or employee code.
step
Select Location/Building
Select the appropriate branch or office building for which you need to create the MIS report.
step
Select Department
If the company has multiple departments, filter for the department for which you need to create an MIS report. You can also select multiple departments at once.
step
Select Employee(s)
The same department could include multiple employees working different shifts. Select the appropriate ones for the monthly muster report creation.
step
Download MIS Report
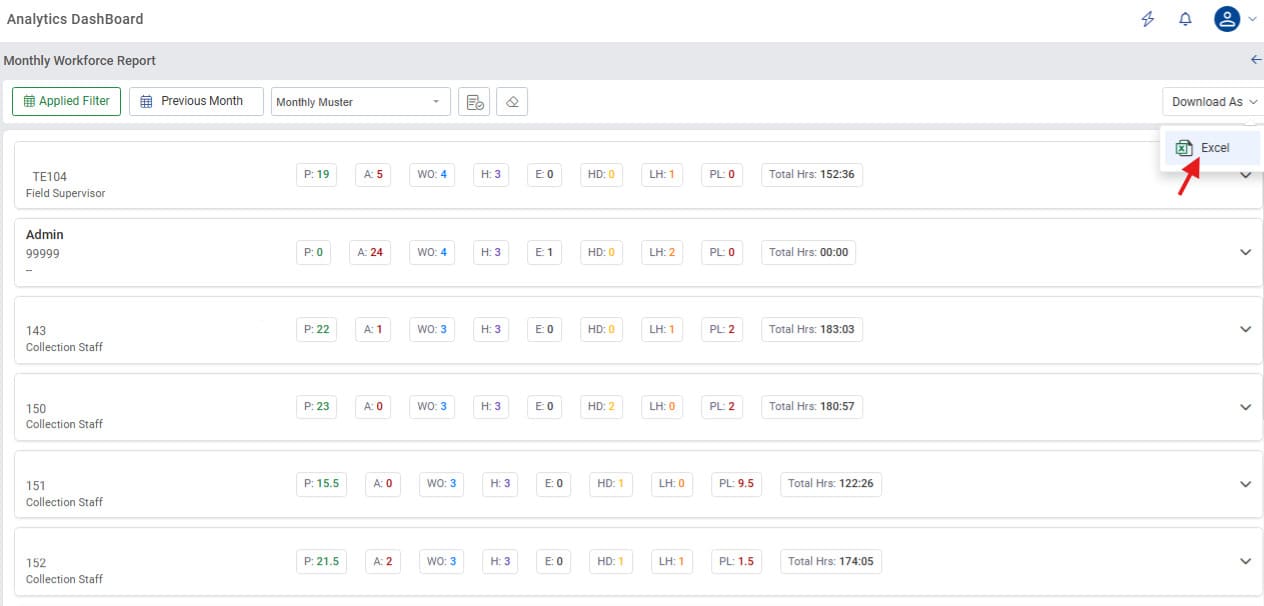
Minop’s analytical dashboard provides a download button to convert all the filtered data into Excel sheets for the creation of comprehensive MIS reports. In retrospect, the accounts team does not have to cross-verify the data with the recorded punch-ins since this data is captured by biometrics.
Related: Salary Arrears in India: Meaning, Calculation, Format & Tax Rules Explained
6 Essential KPIs to Mention in an HR MIS Report
It is one thing to create a report from scratch or merge different reports, but the data inside those reports must clearly reflect everything about the employee while answering incoming questions without becoming too complex. At this point, it is important to know which KPIs your MIS report should address.
Here are the critical KPIs your reports must include:
Actual Present Days:
This directly determines the base salary payable. For monthly-paid employees: (Present Days / Working Days) × Monthly Salary.
Overtime Hours:
This KPI tracks all hours worked beyond an employee's regular shift. It is crucial for immediate operational oversight to manage workloads and ensure accurate payroll calculations.
Late Arrival / Punctuality Rate:
Persistent late arrivals can trigger salary deductions based on policy and often indicate discipline concerns or genuine challenges, such as transport issues or personal circumstances. When viewed by department, late arrival patterns may also reveal shift-related problems that need attention.
Loss of Pay (LOP) Days:
LOP days lead to direct payroll deductions, which must be clearly communicated to employees before salary processing. These deductions usually require managerial approval or confirmation. Since LOP can often be disputed by employees, proper documentation and traceability in the MIS report are essential.
Leave Days by Type:
Since the final payroll depends on an accurate count of present days, it is important for the accounts team or the HR team to receive clear confirmation of paid and unpaid leave from the reporting manager. Every MIS report should clearly mention which leave types were used and how many paid leaves are still available.
Leave Balance:
Leave balance determines whether an employee is eligible to take leave in the upcoming month. It also affects leave encashment calculations during resignation and is an important compliance requirement, as companies must track and report available leave. From a financial standpoint, unused leave becomes a liability on the company’s balance sheet, so accurate reporting is crucial.
Final Thoughts
Having the right data which is formatted correctly, available instantly, and accurate every time is the sign of a proper MIS report. If you're still manually compiling attendance data for payroll, it's time to upgrade. Your finance team deserves timely data, your employees deserve accurate pay, and you deserve to work on HR initiatives that actually matter.
Having the right data formatted correctly, instantly accessible, and consistently accurate is the hallmark of a proper MIS report. If you're still manually compiling attendance data for payroll, it’s time to upgrade to a smarter system. Modern payroll management software not only automates data collection but also eliminates repetitive errors that slow down HR operations. Your finance team deserves timely, reliable data, your employees deserve accurate pay every cycle, and you deserve to focus on HR initiatives that actually move the organisation forward.
FAQs
What is the full form of an MIS report?
MIS stands for Management Information System. An MIS report in HR is a structured document that consolidates time and attendance data into an organized format that supports payroll processing, compliance tracking, and management decision-making.
What is the meaning of an MIS report in an HR context?
In HR operations, an MIS report specifically refers to a pre-processed summary of workforce attendance data that is ready for immediate action. Unlike raw data exports that list individual punch records, an MIS report provides calculated totals, applied policy rules, and formatted summaries that HR teams can directly use for payroll inputs, compliance documentation, or performance reviews.
How do I prepare an MIS report manually?
Collect raw data from biometric devices, leave applications, and employee master records. Calculate metrics like working days, present days, leaves by type, overtime hours, and LOP days. Format the data for payroll by creating employee-wise summaries with all pay-relevant components. Validate by cross-checking totals, spot-checking employees, and getting manager approvals.
Can I filter MIS reports by department, employee, or date range?
Yes, and this is one of the most powerful features of modern HRMS platforms. You can filter MIS reports by specific dates, weeks, months, quarters, financial years, or custom ranges; single or multiple departments with sub-department drill-downs; day shift, night shift, rotating shifts, flexible schedules; and much more.
Can MIS reports integrate directly with payroll software?
Yes, most modern cloud-based HRMS platforms offer direct integration with popular payroll systems. Instead of downloading an MIS report and manually uploading it to your payroll software, the systems communicate directly via API. If direct integration isn't available, most HRMS platforms can export MIS reports in formats compatible with your payroll software's import requirements (e.g., CSV, Excel with specific column structures).

Comments