How Biometrics Improve Workplace Safety?
Posted On:- 12 August, 2025 By:- Vaibhav Maniyar
Introduction
The modern definition of a "safe workplace" has evolved far beyond fire drills and ergonomic chairs. Today, it hinges on a critical concept: digital trust.
In a world where security breaches are not a matter of if but when, businesses are facing unprecedented threats. In fact, a 2023 report highlighted that the average cost of a data breach reached an all-time high of $4.45 million. Traditional security measures like keycards and passwords have becomes liabilities. They can be lost, stolen, or shared, creating vulnerabilities that bad actors are quick to exploit.
This is where biometric technology emerges as a transformative solution. By authenticating identity based on unique biological traits, biometrics provide a definitive, non-transferable method of access control. It’s a shift from protecting a credential to verifying a person, establishing a new gold standard for both physical and digital security.
Role of Biometrics in Workplace Safety
Biometric technology strengthens workplace security in several distinct and impactful ways that legacy systems simply cannot match. Its core function is to ensure that the individual seeking access is precisely who they claim to be, directly tackling the most common security loopholes.
Granting Access Based on Confirmed Identity
The fundamental weakness of keycards and passwords is that they are not permanently tied to an individual. A keycard can be stolen, and a password can be phished. Biometric identifiers, however, are virtually impossible to replicate on the spot. This provides the highest level of assurance for controlling entry to your facilities and sensitive zones.
Protecting Your Most Valuable Asset: Digital Information
Workplace safety today is as much about safeguarding data as it is about securing doors. Integrating biometrics into computer logins and software access—often as a key component of Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA), creates a formidable barrier against cyber threats. Research from Gartner predicts that by 2025, 50% of the workforce will use their primary packaged business applications without ever typing a password. Even if a cybercriminal acquires an employee's password, they cannot breach the system without the required biometric factor, effectively neutralizing the threat.
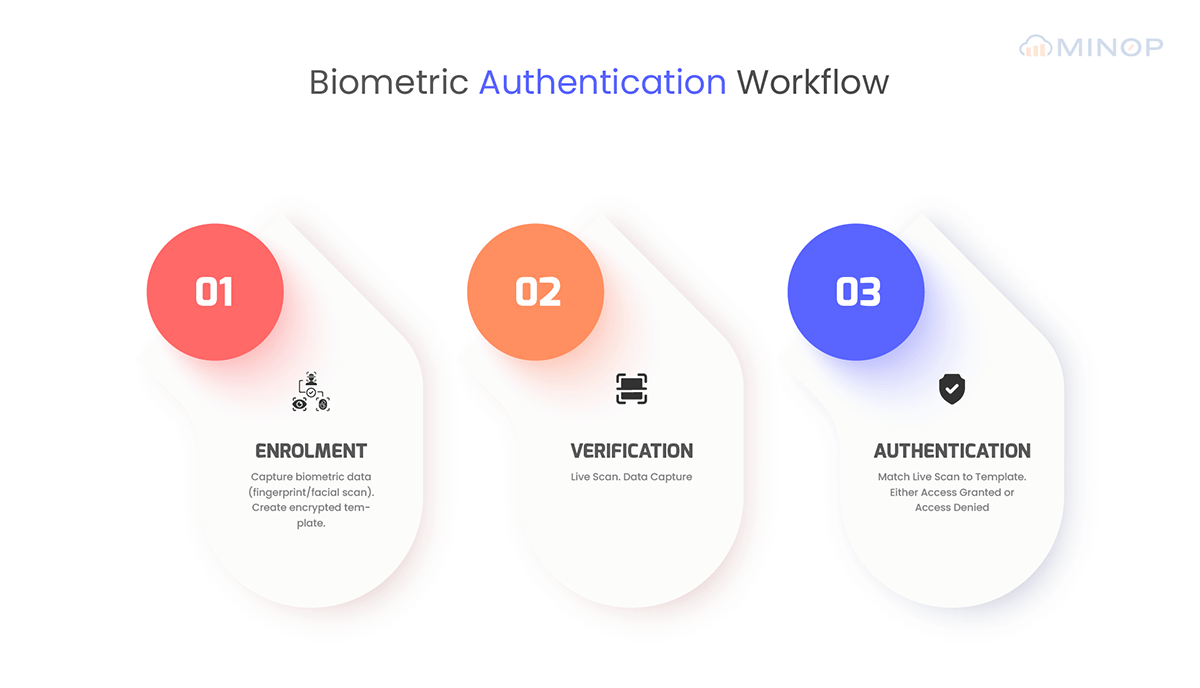
Granting Access Based on Confirmed Identity
When a security incident occurs, the immediate question is always, "Who did what, and when?" With traditional keycards, you only know which card was used, not who used it. Biometrics provide a definitive answer by linking every access event to a specific individual at a precise time. This creates an unchangeable audit trail that is invaluable for investigations, ensuring accountability, and simplifying regulatory compliance.
Securing High-Risk Areas with Granular Control
Not all areas in a workplace are created equal. A server room, a research lab, or a finance department requires far stronger protection than a lobby. Biometric systems excel at providing granular control, allowing you to implement the highest security measures for your most critical assets while maintaining more convenient access for common areas. This ensures security is both robust and intelligently applied.
How Biometrics Impact Workplace Culture
Implementing new security technology is not just a technical decision—it's a cultural one. When introduced thoughtfully, biometrics can significantly improve the work environment.
Fostering Psychological Safety:
Visible and effective security measures make employees feel genuinely safer. This sense of psychological safety is crucial for boosting morale and productivity. Knowing that the workplace is protected by a system that cannot be easily compromised allows team members to concentrate on their work with greater peace of mind.
Demonstrating a Commitment to Employee Well-being:
Investing in advanced technology like biometrics sends a powerful message that the company values its people and is dedicated to providing a safe, modern, and professional environment. It shows that employee safety is a top priority, not merely an afterthought.
Building Trust Through Fairness and Transparency:
Biometric systems can enhance fairness in the workplace. For instance, using a biometric time clock eliminates any disputes over clock-ins and clock-outs, ensuring that all employees are compensated accurately for their time. This builds trust, but it must be accompanied by transparency. It is vital for leadership to communicate clearly about what data is being collected, how it is being used, and the measures in place to protect it.
Creating a Frictionless and Efficient Workplace:
Convenience is a powerful, though often overlooked, cultural benefit. Eliminating the minor, daily frustrations of fumbling for a keycard or trying to remember a forgotten password streamlines the workday. A seamless entry process respects employees' time and contributes to a more efficient and less stressful environment.
Do Biometric Access Controls Really Deliver?
In a world where businesses are striving to enhance security without complicating daily operations, biometrics offer a clear advantage. Here are the practical benefits of integrating biometric systems in the workplace.

Unparalleled Security:
Keys and access cards can be lost, shared, or stolen. Biometric identifiers are unique to an individual, meaning they cannot be passed around. This is a simple yet powerful way to ensure that only authorized personnel gain access, eliminating the persistent worry of lost badges and unauthorized entry.
Boosted Efficiency:
Imagine the morning rush at the office entrance. Instead of a queue of people searching for their badges, everyone can move through smoothly with a quick scan. Those seconds saved per person, every day, accumulate into significant gains in productivity and a reduction in daily hassle.
Enhanced User Experience:
There's no denying the modern appeal of using a fingerprint or a facial scan to open a door. It lends a tech-savvy and forward-thinking vibe to the workplace that both employees and visitors notice. This small touch demonstrates that your company is innovative and values a seamless experience.
Reduced Administrative Burdens:
Consider the time your administrative team spends issuing new cards, deactivating lost ones, and managing access permissions. Biometric systems simplify these tasks immensely. Onboarding a new employee or revoking access for a departing one can be done in seconds from a centralized platform, freeing up your team to focus on more strategic responsibilities.
Scalability and Flexibility:
As your business grows and changes, your security system must be able to adapt. Whether you're expanding to a new floor, hiring a new team, or increasing security in a specific area, a biometric system can be easily reconfigured to meet your evolving needs.
Long-Term Cost Savings:
While there is an initial investment, the long-term savings are substantial. You can eliminate the recurring cost of purchasing replacement keycards and prevent financial losses from issues like time theft. Most importantly, you drastically reduce the risk of a costly security breach, making biometrics a wise financial investment.
Related: What is a Biometric Attendance System?
How Multimodal Biometrics Are Taking Over?
To protect high-value assets, relying on a single biometric factor is becoming insufficient. The market is shifting toward multimodal biometrics, which layer two or more credentials to create a significantly more robust security posture.
For instance, a data center might require both an iris scan and a palm vein reading for entry, making a breach exponentially more difficult. According to a report from MarketsandMarkets, the multimodal biometrics market is projected to grow from USD 2.5 billion in 2022 to USD 8.9 billion by 2027, signaling a clear industry shift toward these layered defenses. This isn't just about security; it's about context. Access to a general office might only require a facial scan, but accessing the server room could trigger a secondary request for a voice command, applying friction intelligently where the risk is highest.
The rise of AI-generated deepfakes and sophisticated 3D masks has made it critical to determine that a biometric trait is being presented by a live person. This is where advanced liveness detection becomes non-negotiable. Modern systems use AI to analyze subtle, involuntary cues that are invisible to the human eye, such as microscopic eye movements, skin texture reflections, and blood flow patterns under the skin (as detected by infrared sensors).
This technology is the frontline defense against "presentation attacks," ensuring that a high-resolution photo or video of an employee cannot be used to fool the system. For instance, the system could flag an employee attempting to access a sensitive database at an unusual time or from a new location.
A 2023 IBM report found that organizations using extensive security AI and automation identified and contained breaches 108 days faster than those without, underscoring the practical impact of proactive security analytics. This allows security teams to intervene before a potential incident escalates into a full-blown breach.
Conclusion
When employees feel secure, they are more focused, collaborative, and engaged. In the modern business world, being "safe" extends beyond physical security to encompass the protection of data, the integrity of operations, and the psychological well-being of the team.
That’s where Minop steps in. As a cloud-based time and attendance software, Minop ensures that workplace security is about building trust. From safeguarding employee data to ensuring transparent attendance tracking, Minop helps organizations create an environment where people feel valued, protected, and empowered to do their best work.
FAQs
Why are businesses moving beyond traditional passwords and keycards to biometrics?
Organizations are shifting to stronger access controls because traditional methods like passwords and ID cards are no longer sufficient. These credentials can be lost, stolen, shared, or duplicated, creating significant security vulnerabilities. Biometric systems address these weaknesses by linking access directly to an individual's unique biological traits, ensuring that only verified personnel can access sensitive physical locations and critical company networks. This technology also prevents issues like "buddy punching," where employees clock in for one another, leading to more accurate time and attendance tracking.
Are biometric systems safe for employee privacy?
Yes, when implemented with modern technology and clear policies. Biometric systems do not store actual images of fingerprints or faces. They convert this data into an encrypted mathematical template that cannot be reverse-engineered to recreate the original image. This ensures employees' personal biological data remains private. Furthermore, laws in many regions require companies to obtain written consent from individuals before collecting their biometric data and to have clear policies on how the data is stored, used, and eventually destroyed.
What makes modern biometric systems so difficult to "spoof" or trick?
Early systems may have been vulnerable, but modern biometric scanners incorporate sophisticated "liveness detection" technology. This feature uses advanced algorithms and AI to distinguish between a live person and a fraudulent representation, such as a high-resolution photograph, a 3D mask, or a silicone fingerprint replica. Liveness detection analyzes subtle cues like blinking, facial movements, or blood flow patterns, making today's high-quality systems extremely resistant to spoofing attempts.
What are the legal responsibilities for a company using employee biometric data?
Companies that collect and use biometric data have significant legal obligations that vary by location. In many jurisdictions, employers must first inform employees in writing that their data is being collected and stored. They must also specify the purpose and length of time for which the data will be kept and obtain written consent from the employee. It is crucial for businesses to establish clear policies for the secure storage and eventual destruction of this sensitive information to comply with regulations like the Biometric Information Privacy Act (BIPA) in Illinois and the GDPR in Europe.
Which biometric technology is the "best" for a workplace?
There is no single "best" technology, as the ideal choice depends on a company's specific needs. Fingerprint recognition is mature, widely adopted, and cost-effective. Facial recognition offers a convenient, touchless experience suitable for many office environments. For higher security needs, technologies like iris or palm vein recognition are exceptionally accurate and difficult to replicate. The optimal solution involves balancing the required security level with user convenience, the physical environment, and overall cost.
What happens if a biometric system fails or can't read an employee's data?
Biometric systems are highly reliable but not foolproof; issues like scanner malfunctions or difficulty reading an individual's trait due to injury can occur. For this reason, it is essential to have backup procedures. Most organizations implement a multi-faceted approach, such as providing an alternative verification method managed by security or HR personnel or issuing temporary access credentials after a manual identity check. This ensures that a technical glitch does not prevent legitimate access or disrupt workflow.

Comments